Azure Login Portal: 7 Ultimate Tips for Seamless Access
Accessing the Azure login portal doesn’t have to be complicated. Whether you’re a developer, IT admin, or business user, mastering this gateway is essential for managing cloud resources efficiently and securely. Let’s break down everything you need to know.
Understanding the Azure Login Portal
The Azure login portal is the primary entry point for accessing Microsoft Azure services. It serves as a centralized dashboard where users authenticate and manage cloud infrastructure, applications, and data. Millions of users interact with the Azure login portal daily to deploy virtual machines, configure networks, monitor performance, and more.
What Is the Azure Login Portal?
The Azure login portal, commonly accessed via portal.azure.com, is a web-based interface provided by Microsoft for managing Azure cloud services. It combines identity authentication with resource management, allowing users to securely log in using their Microsoft accounts or organizational credentials.
- It supports multi-factor authentication (MFA) for enhanced security.
- Users can access it from any modern browser on desktop or mobile devices.
- The portal integrates with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) for identity and access management.
How Does It Differ From Other Microsoft Logins?
While Microsoft offers several login interfaces—such as Office 365, Xbox, or Outlook—the Azure login portal is specifically designed for cloud infrastructure management. Unlike consumer-focused portals, it provides deep administrative controls, role-based access, and real-time monitoring tools.
“The Azure portal isn’t just a login page—it’s a command center for your entire cloud ecosystem.” — Microsoft Cloud Documentation
Step-by-Step Guide to Accessing the Azure Login Portal
Logging into the Azure portal is straightforward, but understanding each step ensures a smooth experience, especially for first-time users or those managing multiple subscriptions.
Navigating to the Official Login Page
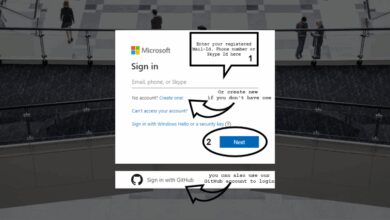
To begin, open your preferred web browser and go to https://portal.azure.com. This is the official URL for the Azure login portal. Avoid third-party links or search engine ads that may lead to phishing sites.
- Bookmark the correct URL to prevent accidental visits to fake portals.
- Ensure your browser is up-to-date to support modern authentication protocols.
- Use private/incognito mode if logging in from a shared device.
Entering Your Credentials
Once on the login page, enter your email address associated with your Azure account. This could be a personal Microsoft account (e.g., @outlook.com) or a work/school account (e.g., @yourcompany.com).
- If you’re part of an organization, use your corporate email linked to Azure AD.
- After entering your email, click “Next” and input your password.
- For added security, enable biometric authentication if supported by your device.
Completing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Most enterprise and admin accounts require MFA. After entering your password, you’ll be prompted to verify your identity through a second method:
- Microsoft Authenticator app notification
- SMS code sent to your registered phone
- Email verification link
- Hardware security key (e.g., YubiKey)
Choose the method configured by your administrator. Once verified, you’ll gain access to the Azure dashboard.
Common Issues When Using the Azure Login Portal
Despite its reliability, users occasionally face obstacles when trying to log in. Understanding these issues helps reduce downtime and frustration.
Forgot Password or Locked Account
One of the most frequent problems is forgetting your password or getting locked out due to multiple failed attempts. The Azure login portal includes self-service password reset (SSPR) for eligible accounts.
- Click “Forgot password?” on the login screen.
- Follow the prompts to verify your identity via email, phone, or security questions.
- Reset your password and log back in.
If SSPR isn’t enabled, contact your Azure administrator for assistance.
Browser Compatibility and Cache Issues
Sometimes, the issue isn’t with credentials but with the browser itself. Outdated browsers or corrupted cache can prevent proper loading of the Azure login portal.
- Use supported browsers: Chrome, Edge, Firefox, or Safari.
- Clear cookies and cache before attempting to log in.
- Disable browser extensions that might interfere with authentication flows.
Tip: Try accessing the portal in incognito mode to rule out extension conflicts.
Multi-Factor Authentication Failures
MFA failures are common, especially if your phone is lost, the authenticator app isn’t syncing, or SMS delivery is delayed.
- Ensure your trusted devices and methods are up to date in Azure AD.
- Register backup MFA options like a secondary phone or email.
- Contact your IT department if you’re unable to complete MFA.
Security Best Practices for the Azure Login Portal
Given that the Azure login portal grants access to critical cloud assets, securing your login process is non-negotiable. Follow these best practices to protect your environment.
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication
MFA is one of the most effective ways to prevent unauthorized access. Even if a password is compromised, attackers cannot log in without the second factor.
- Enforce MFA for all users, especially administrators.
- Use the Microsoft Authenticator app instead of SMS for better security.
- Consider passwordless authentication options like FIDO2 security keys.
Use Conditional Access Policies
Conditional Access in Azure AD allows organizations to control how and when users can access the Azure login portal based on specific conditions.
- Restrict logins to specific IP ranges or geographic locations.
- Block access from unmanaged or non-compliant devices.
- Require MFA when accessing sensitive resources or from unfamiliar networks.
These policies are configured under the Azure Active Directory section of the portal.
Monitor Sign-In Logs and Alerts
Azure provides detailed sign-in logs that help detect suspicious activity. Regularly reviewing these logs can prevent breaches.
- Navigate to Azure AD > Monitoring > Sign-in logs.
- Filter logs by user, app, status (success/failure), or risk level.
- Set up alerts for failed login attempts or logins from unusual locations.
Integrate with Microsoft Defender for Cloud for advanced threat detection.
Customizing Your Azure Portal Experience
Once logged in, the Azure portal can be tailored to suit your workflow. Personalization improves efficiency and reduces navigation time.
Pinning Resources to the Dashboard
The Azure dashboard is fully customizable. You can pin frequently used resources, such as virtual machines, storage accounts, or databases, for quick access.
- Open the resource you want to monitor.
- Click “Pin to dashboard” in the top menu.
- Choose which dashboard to pin it to (default or custom).
You can also resize and rearrange tiles for optimal layout.
Creating Custom Dashboards
Teams or individuals managing different sets of resources can create separate dashboards.
- Click “New dashboard” on the homepage.
- Add widgets like cost analysis, resource health, or custom queries.
- Share dashboards with team members for collaborative monitoring.
This is especially useful for DevOps teams or departments with distinct responsibilities.
Using Azure Cloud Shell
The Azure Cloud Shell is a browser-based command-line interface accessible directly from the portal. It supports both Bash and PowerShell.
- Click the Cloud Shell icon (>_ ) in the top navigation bar.
- Choose your preferred shell environment.
- Run CLI or PowerShell commands without installing anything locally.
Your files are stored in an Azure file share, making them persistent across sessions.
Managing Multiple Subscriptions via the Azure Login Portal
Organizations often have multiple Azure subscriptions—for different departments, projects, or environments (dev, test, prod). Managing them efficiently is crucial.
Switching Between Subscriptions
After logging into the Azure login portal, you can switch between subscriptions using the directory + subscription selector in the top-right corner.
- Click your profile icon and select “Switch directory” or “Change directory”.
- Choose the subscription you want to work with.
- The portal interface updates to reflect resources in the selected subscription.
This is essential for administrators managing hybrid or multi-tenant environments.
Setting Default Subscription Preferences
To avoid confusion, set a default subscription so you land in the right place after login.
- Go to your account settings in the portal.
- Select the preferred subscription as default.
- Save changes—this will apply across devices and sessions.
This feature is particularly helpful for consultants or freelancers working across clients.
Using Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC allows fine-grained permission management across subscriptions. You can assign roles like Owner, Contributor, or Reader to users or groups.
- Navigate to the subscription > Access control (IAM).
- Add a role assignment by selecting a user and role.
- Use built-in roles or create custom ones for specific needs.
Proper RBAC setup prevents privilege escalation and ensures compliance.
Advanced Features Accessible Through the Azure Login Portal
Beyond basic login and navigation, the Azure login portal unlocks powerful tools for automation, monitoring, and governance.
Azure Monitor and Alerts
Azure Monitor collects telemetry from your resources, helping you detect issues before they impact users.
- Set up metric alerts for CPU usage, memory, or network latency.
- Create activity log alerts for configuration changes.
- Use Log Analytics to run advanced queries on operational data.
All of this is accessible directly after logging into the Azure portal.
Automation with Azure Logic Apps and Runbooks
Automate repetitive tasks like starting/stopping VMs, sending notifications, or syncing data.
- Create Logic Apps for workflow automation across services.
- Use Azure Automation runbooks (PowerShell or Python) for scheduled tasks.
- Trigger automations based on events or schedules.
These tools reduce manual errors and improve operational efficiency.
Cost Management and Budgeting
The Azure portal includes robust cost management tools to track spending and optimize usage.
- View detailed cost analysis by service, region, or tag.
- Set monthly budgets with alert thresholds.
- Identify idle or underutilized resources for shutdown.
Link your Azure account to Microsoft Cost Management for enterprise-grade reporting.
Troubleshooting and Support Options for the Azure Login Portal
Even with best practices, issues can arise. Knowing where to get help is critical.
Using the Azure Help + Support Center
After logging in, access the Help + Support blade from the left navigation menu.
- Search the knowledge base for common issues.
- Open a support ticket if you need direct assistance.
- Check service health for ongoing outages.
Paid support plans offer faster response times and technical advisor access.
Community Forums and Documentation
Microsoft hosts active community forums where users share solutions.
- Visit Microsoft Q&A for peer support.
- Refer to official Azure documentation for step-by-step guides.
- Join Azure-focused groups on Reddit or Stack Overflow.
Many login issues have already been solved by others in the community.
Contacting Azure Support Directly
For urgent issues—like being locked out of an admin account—contact Azure support directly.
- Go to Help + Support > New support request.
- Select the issue type (e.g., account, billing, technical).
- Provide details and choose your contact method (email, phone, chat).
Enterprise customers can use Premier Support for 24/7 access.
What is the correct URL for the Azure login portal?
The official URL is https://portal.azure.com. Always verify the domain to avoid phishing scams.
Why can’t I log in to the Azure portal?
Common reasons include incorrect credentials, expired passwords, MFA setup issues, or browser problems. Try resetting your password, clearing cache, or using a different device.
How do I enable multi-factor authentication for my Azure account?
Go to Azure Active Directory > Security > Multi-Factor Authentication. Follow the prompts to enable MFA for users. Admins can enforce it via Conditional Access policies.
Can I access the Azure portal on mobile?
Yes, the Azure portal is mobile-responsive. You can also download the Microsoft Azure app from the App Store or Google Play for a streamlined experience.
What should I do if I lose my MFA device?
If you lose your MFA device, use a backup method (like a secondary phone or email) to log in. If none are available, contact your Azure administrator to reset your MFA settings.
Mastering the Azure login portal is the first step toward unlocking the full potential of Microsoft’s cloud platform. From secure authentication to managing complex multi-subscription environments, the portal serves as your gateway to scalable, reliable, and intelligent cloud solutions. By following best practices in security, customization, and troubleshooting, you can ensure seamless access and optimal performance. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned pro, continuous learning and adaptation are key to staying ahead in the cloud era.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: